Download Throttlestop – A powerful utility designed to monitor and control your CPU’s performance on Windows-based laptops and desktops.
The software provides control over various parameters like voltage, clock speed, and power limits, helping users prevent or reduce throttling—a condition where the CPU reduces its speed to avoid overheating or exceeding power limits.
What is Throttlestop?
ThrottleStop is a lightweight application developed by Kevin Glynn that allows users to fine-tune their CPU’s performance settings. The software provides control over various parameters like voltage, clock speed, and power limits, helping users prevent or reduce throttling—a condition where the CPU reduces its speed to avoid overheating or exceeding power limits.
Why Use ThrottleStop?
ThrottleStop is particularly useful in scenarios where your CPU’s performance is being limited by factory settings, thermal constraints, or power limits. This can happen in a variety of situations:
- High-Performance Laptops: Many high-end laptops are designed to run at lower speeds to manage heat and power consumption. ThrottleStop can help unlock their full potential, especially in gaming laptops that need maximum performance.
- Overclocking Enthusiasts: For users looking to push their hardware beyond its stock capabilities, ThrottleStop provides a safer and more controlled environment for overclocking.
- Older Hardware: On older systems where manufacturers implemented conservative power and thermal limits, ThrottleStop can help maintain better performance over time.
- Undervolting for Cooler Operation: By undervolting, users can achieve a cooler and quieter system, which is especially beneficial in compact or thermally constrained environments like ultrabooks or small form factor desktops.
Key Features
ThrottleStop offers a variety of features that enable users to customize and optimize their CPU performance. Some of the most significant features include:
1. Monitoring and Logging
ThrottleStop provides real-time monitoring of CPU temperatures, clock speeds, and power consumption. It can display important details such as the current CPU frequency, voltage, and the state of thermal throttling. Additionally, ThrottleStop allows users to log this data for later analysis, which can be particularly useful for identifying performance bottlenecks or understanding how the CPU behaves under different workloads.
2. Thermal Throttling Management
Thermal throttling is a mechanism used by CPUs to prevent overheating by reducing the clock speed when temperatures exceed safe levels. While this protects the CPU, it can also lead to significant performance drops. ThrottleStop enables users to override or adjust these throttling limits, allowing the CPU to maintain higher clock speeds even under load. This feature is particularly useful for users who have adequate cooling solutions in place and want to extract maximum performance from their hardware.
3. Voltage Control (Undervolting)
ThrottleStop allows users to adjust the CPU’s voltage settings, specifically enabling undervolting. Undervolting involves reducing the voltage supplied to the CPU, which can lower power consumption and reduce heat generation without significantly impacting performance. This is especially beneficial for laptops, as it can lead to longer battery life and cooler operation. It’s worth mentioning that while undervolting can be safe, overdoing it may cause system instability, so users need to proceed with caution.
4. Power Limit Adjustment
Many CPUs, particularly those in laptops, come with power limits set by the manufacturer to balance performance, heat, and battery life. ThrottleStop allows users to tweak these power limits, which can either increase performance (by allowing the CPU to consume more power) or improve efficiency (by reducing power consumption). Users can set different power limits for various usage scenarios, giving them more control over how their CPU behaves.
5. SpeedStep and Turbo Boost Management
Intel’s SpeedStep and Turbo Boost technologies dynamically adjust the CPU clock speed based on the workload. ThrottleStop provides options to enable, disable, or fine-tune these features. For example, users can disable Turbo Boost to keep the CPU running at a consistent speed, which might be preferable in certain scenarios, or they can ensure Turbo Boost is always enabled for maximum performance.
6. Profiles and Customization
ThrottleStop supports the creation of multiple profiles, each with its own settings. This allows users to switch between different performance modes easily, such as a high-performance mode for gaming and a power-saving mode for casual use. Profiles can be customized extensively, giving users the flexibility to optimize their CPU settings for specific tasks.
How Throttlestop Works?
ThrottleStop interacts directly with your CPU’s registers, allowing it to override default settings and provide you with more control over performance parameters. Below, we delve into some of the key components of ThrottleStop and how they work.
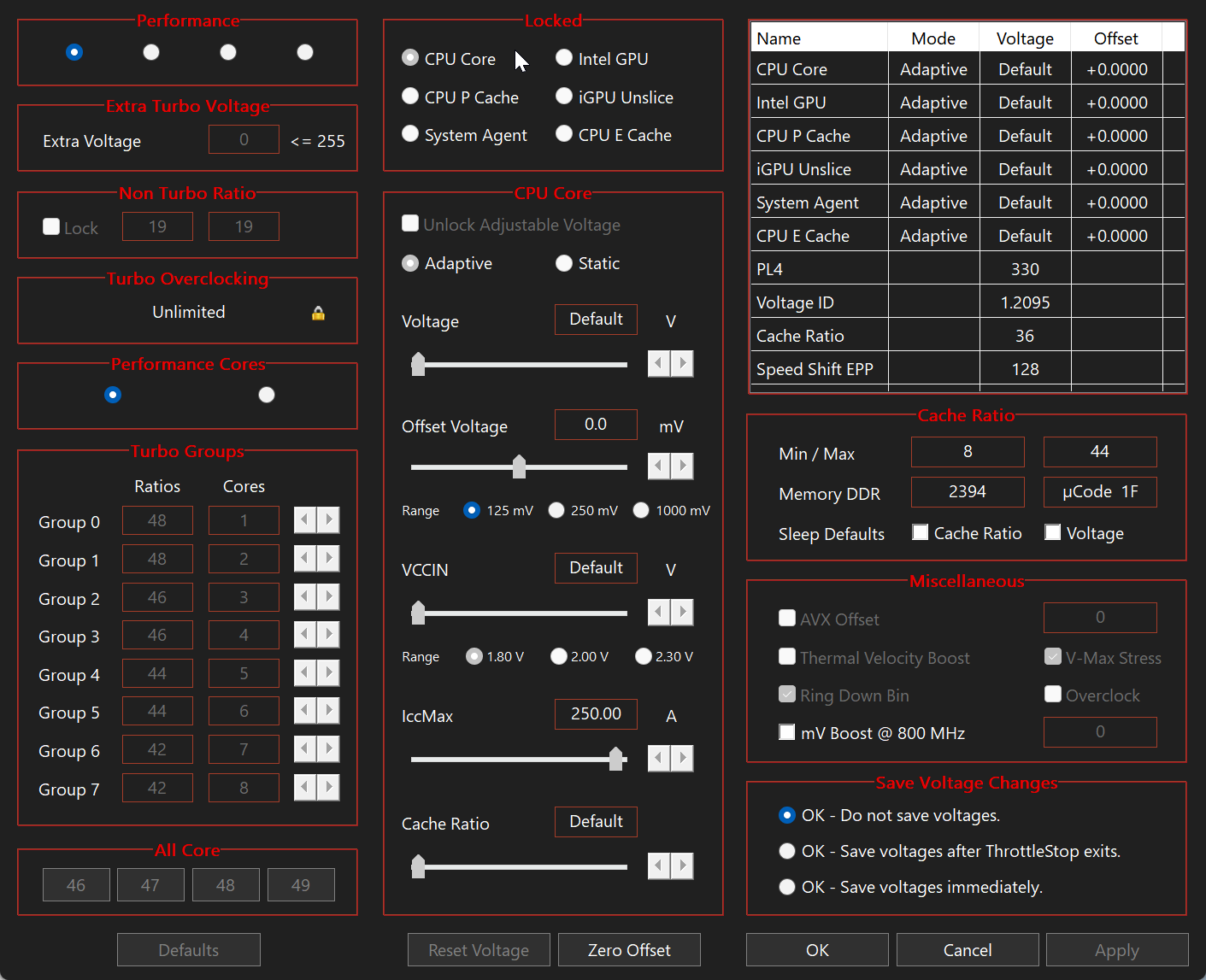
1. The Main Window: A Dashboard for Control
The main window of ThrottleStop is your command center. It displays vital statistics and provides access to the primary functions of the software. Here’s a breakdown of the main sections:
- Monitoring Panel: Displays real-time data including CPU temperature, clock speed, and power consumption.
- Profile Buttons: Allows you to switch between different performance profiles.
- Clock Modulation: Provides options to control CPU multiplier, TDP (Thermal Design Power), and Turbo Boost.
- BD PROCHOT: Toggle the BD PROCHOT feature on or off, as mentioned earlier.
2. Profiles: Tailor Performance to Your Needs
ThrottleStop’s profile system is one of its most powerful features. You can create up to four different profiles, each with its own set of performance parameters.
- Performance Profile: Designed for maximum CPU speed and power, ideal for gaming or demanding applications.
- Battery Saver Profile: Reduces power consumption by lowering clock speeds and disabling Turbo Boost, useful when you’re running on battery power.
- Balanced Profile: Offers a middle ground between performance and power saving.
- Cool Profile: Focuses on keeping your system cool by lowering voltage and clock speed, reducing heat output.
You can switch between these profiles manually or use the task scheduler to switch automatically based on the application you’re running.
3. Undervolting: Reduce Heat and Power Consumption
Undervolting is a technique where you reduce the voltage supplied to your CPU. This can result in lower temperatures and extended battery life without significantly affecting performance. ThrottleStop makes it easy to adjust the voltage offset.
- How to Undervolt:
- Open the FIVR (Fully Integrated Voltage Regulator) control panel.
- Adjust the “Offset Voltage” sliders for both the CPU core and cache.
- Start with a small reduction (e.g., -50 mV) and gradually increase the offset until you find a stable undervolt.
- Benefits:
- Lower temperatures, reducing the risk of thermal throttling.
- Extended battery life on laptops.
- Quieter operation as fans don’t need to work as hard.
- Risks:
- Too much undervolting can lead to system instability. Always test your system’s stability with stress tests after making changes.
4. Turbo Boost Management
Intel’s Turbo Boost technology allows CPUs to exceed their base clock speed under certain conditions, providing a temporary performance boost. However, Turbo Boost can also lead to increased power consumption and heat.
- Enabling/Disabling Turbo Boost: You can choose to enable or disable Turbo Boost depending on your current needs. For example, disabling it while on battery power can extend battery life.
- Customizing Turbo Boost: ThrottleStop allows you to fine-tune when and how Turbo Boost kicks in, giving you control over how much extra performance your CPU can deliver and for how long.
5. BD PROCHOT: Understanding the Risks
BD PROCHOT is a signal that allows other components like the GPU or motherboard to request that the CPU throttle its speed to reduce heat. While disabling BD PROCHOT in ThrottleStop can prevent unnecessary throttling, it comes with risks:
- Heat Buildup: Disabling BD PROCHOT means your CPU might continue running at high speeds even when other components are overheating, potentially leading to hardware damage.
- Use with Caution: Only disable BD PROCHOT if you are confident that your system’s cooling is adequate, and you understand the risks.
How to Set Up Throttlestop?
Setting up ThrottleStop is straightforward, but it requires careful attention to detail to ensure that you’re getting the most out of your CPU without compromising system stability.
1. Download and Install ThrottleStop
ThrottleStop is available as a free download from various tech forums and websites. Once downloaded, extract the files to a folder on your computer.
2. Initial Configuration
- Run ThrottleStop as Administrator: This ensures that the application has the necessary permissions to make changes to your system.
- Configure Profiles: Set up your desired profiles based on your usage scenarios (e.g., gaming, battery saver).
- Adjust Clock Modulation and Set Limits: Depending on your CPU, you can adjust clock speeds, voltage, and power limits to fine-tune performance.
3. Testing and Fine-Tuning
After making adjustments, it’s important to test your system to ensure stability:
- Stress Testing: Use tools like Prime95 or IntelBurnTest to stress your CPU and check for stability issues.
- Temperature Monitoring: Keep an eye on your CPU temperatures using the monitoring tools within ThrottleStop or third-party applications like HWMonitor.
- Fine-Tune: Based on your testing, you may need to fine-tune your settings for the best balance between performance and stability.
4. Setting Up Automatic Profile Switching
For convenience, you can set up ThrottleStop to automatically switch profiles based on the applications you run:
- Task Scheduler: Use Windows Task Scheduler to create tasks that switch profiles when specific programs are launched or closed.
- Third-Party Tools: Some users prefer using third-party tools like EventGhost for more advanced automation.